1、虚拟dom
首先,我们都知道react和vue有一个创建虚拟dom的方法createElement,用法如下:
1 |
|
createElement方法的具体实现:
1 |
|
2、虚拟dom转换成实体dom
1 |
|
接下来我们来分析下,如果根据虚拟dom的解构去比较新旧元素的变化,要采用哪种遍历算法,以及节点的具体修改情况。
3、遍历算法
1)vue和react采用的都是深度遍历算法,同级的比较元素的变化,这样时间复杂度达到O(n)。
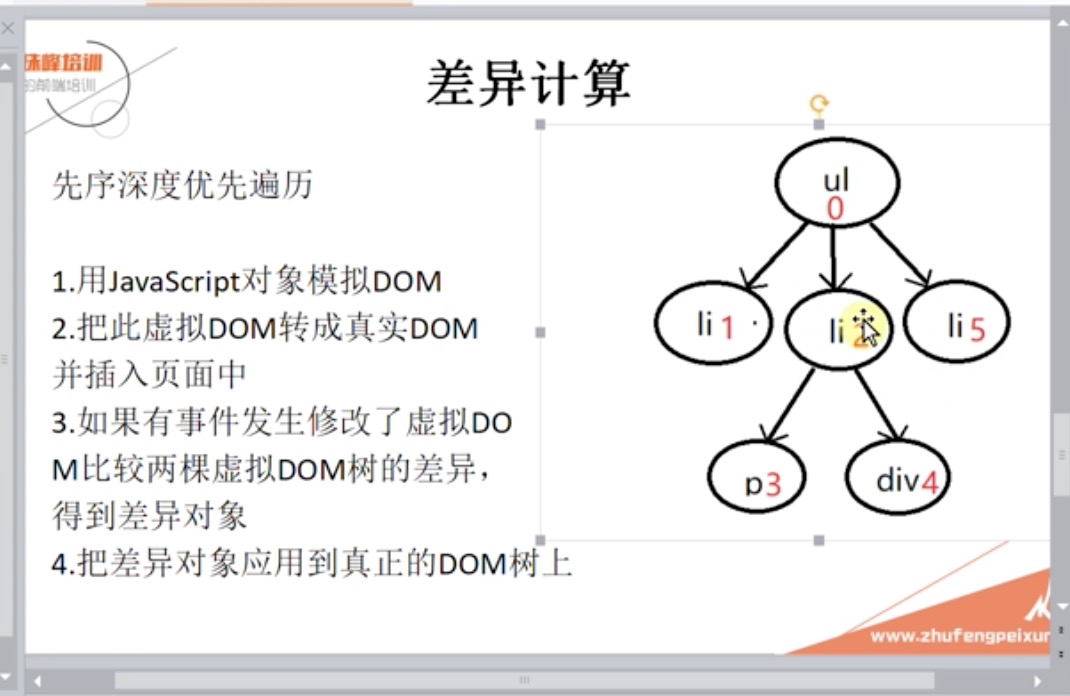
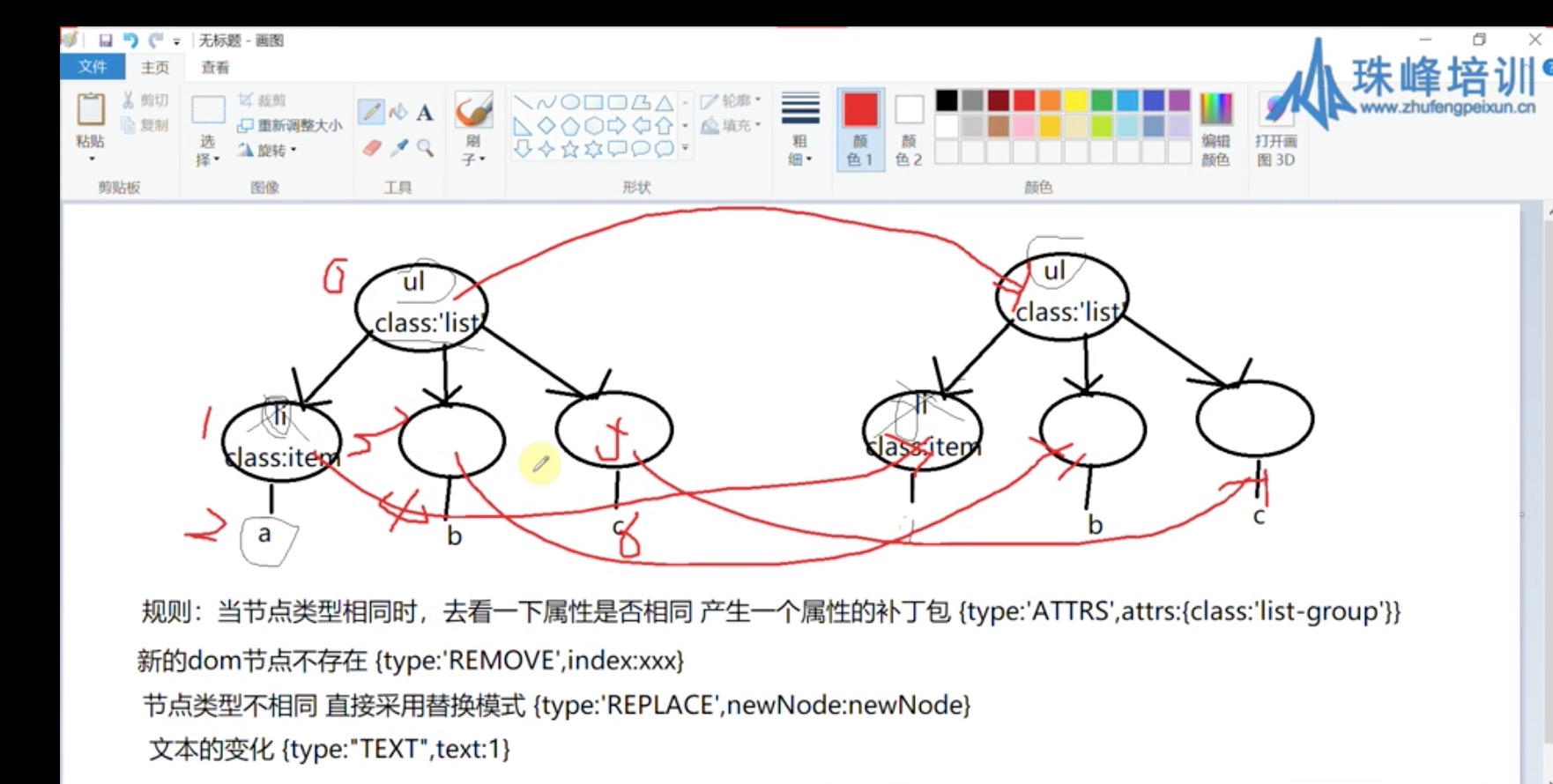
2)分析了节点的修改情况主要有以下几种:
a.当节点数量不发生更改时,且节点类型相同,节点属性发生变化时,产生一个补丁包,形如:{type: ‘ATTRS’,attrs:{class:’list-group’}}
b.当dom发生删减时 {type: ‘REMOVE’,index:xxx}
c.当节点类型不同,代表旧元素被替换 {type: ‘REPLACE’, newNode: newNode}
d.当节点的文本发生变化时,{type:’TEXT’, text: ‘xxx’}
这里暂时不考虑元素位置调换以及增加元素的情况。
下面是新旧绩点比较的代码实现:
1 |
|
最后映射到真实dom的代码:
1 |
|
到这里,一个简单的dom-diff结构就算完成了,(连写好几天递归,再也不怕死循环惹![]() )
)
4、知识点:
1)createTextNode:
可创建文本节点。
2)tagName:
在xml中(或其他语言,如xhtml,xul)文档中,tagName的值会保留原始的大小写; 在html文档中,tagName会返回其大写形式,对于元素节点来说,tagName属性的值和nodeName属性的值是相同的。
tagName只有在元素节点才有值,nodeName在所有节点上都有值。
因此建议可使用nodeName多一些。
3)instanceof:
用于测试构造函数的prototype属性是否存在与对象的原型链的任何位置上。
但需要注意的是:
a.构造函数的prototype不是一成不变的,发生修改后,instanceof检测后的值会发生变化。
b.实例的__proto__也会发生修改(非标准),instanceof检测后的值会发生变化。